Broker & Interface¶
The Broker and Interface are the two fundamental blocks of POP-Java, the former represent the server instance of a POP Object while the latter is the client connecting to it.
Broker¶
The Broker class is a wrapper for an instance of a POP Object. Meaning that each instantiated POP Object will have its own Broker instance associated with it. It is also the entry point for newly created POP Objects.
General architecture¶
As we can see in Figure 1 we have two distinct JVMs, one running the Main of the application while the second running the Broker’s Main.
The Broker’s Main will create a new Broker instance which will be the wrapper for the POP Object requested by the application Main. The instance will open one or more listening ComboxServer which will enable Broker to receive method calls from PJMethodHandler and send them to the wrapped object. See Architecture to understand how POP Objects are created.
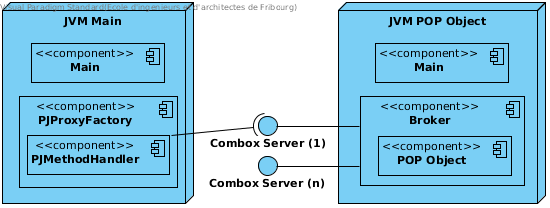
Figure 1: Broker components
Note
PJMethodHandler extends Interface, which is the base of communication with a Broker; without PJMethodHandler is what enable us to make remote calls to methods.
Entry Point¶
A Broker can be create in two ways: as the entry point (main) of a new JVM (Figure 1) or directly by PJProxyFactory if we decide not to create a new dedicated JVM.
Let’s take a look at an example of the former case in a classic scenario, the arguments received by the Broker main are:
-object=MyPopObject
-codelocation=http://myapp.com/app.jar
-callback=socket://IP:PORT1
-appservice=socket://IP:PORT2 ssl://IP:PORT3
-socket_port=0
-ssl_port=0
objectis the name of the class of our POP Object.codelocationtell the Broker where to loadobjectfrom.callbackis an immediate location to report whichComboxServerBrokerhas opened.appservicethe location whereAppServicecan be accessed from.<PROTOCOL>_portopen aComboxServerof typePROTOCOL.
If the user is using a personal POP-Java configuration file and used @POPObjectDescription(url = "localhost") a extra parameter configfile is added with the path to the file which will be loaded by the Broker.
Initialization¶
In both Entry Point`s the method ``public boolean initialize(java.util.List<java.lang.String>);` is called, the main objective of this method is to start ComboxServer in relation to how many <PROTOCOL>_port were supplied.
In the case no particular protocol was supplied, the default one specified in DEFAULT_PROTOCOL will be used.
Note
It’s possible to open multiple ComboxServer of the same type by supplying <PROTOCOL>_port multiple times.
Interface & PJMethodHandler¶
Interface is the class we use to allocate a new JVM and connect to a new POP Object; PJMethodHandler, instead, by extending it, add the ability to invoke the POP Object methods.
Generally Interface enable us only to connect to a POP Object, while PJMethodHandler allow us to use it.
Note
Currently Interface contains multiple static methods used to run a command on the local machine and lauch a new JVM. Those methods, name-wise and location-wise, are confusing and should be moved.